Popular Articles
- Earliest molecular events of vision revealed
- Dynamics and Kinetics in Structural Biology
- Structural biology is solved -- now what?
- XFEL Pulses Demonstrate How Plants Perceive Light
- BioXFEL Postdoctoral Fellowship Award
Archived Articles
News
- Details
- Thursday, 12 January 2017
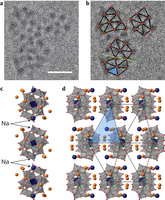
How molecules in solution form crystal nuclei, which then grow into large crystals, is a poorly understood phenomenon. The classical mechanism of homogeneous crystal nucleation proceeds via the spontaneous random aggregation of species from liquid or solution. However, a non-classical mechanism suggests the formation of an amorphous dense phase that reorders to form stable crystal nuclei. So far it has remained an experimental challenge to observe the formation of crystal nuclei from five to thirty molecules.
- Details
- Tuesday, 10 January 2017
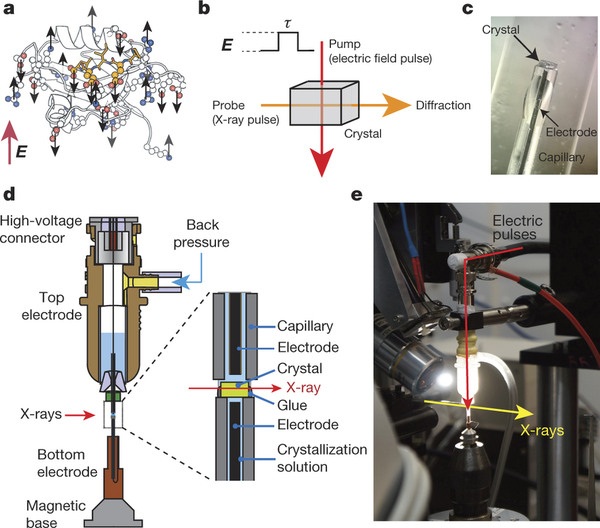
A new imaging technique to see proteins live in motion has been developed. The feat achieved by researchers at the UT Southwestern Medical Center comes as a response to electric field pulses and X-rays acting on protein particles.
Given that subtle motions govern protein functions that take place on nano time scales of trillionths of a second, the study offers great potential in knowing how proteins work.
- Details
- Tuesday, 03 January 2017
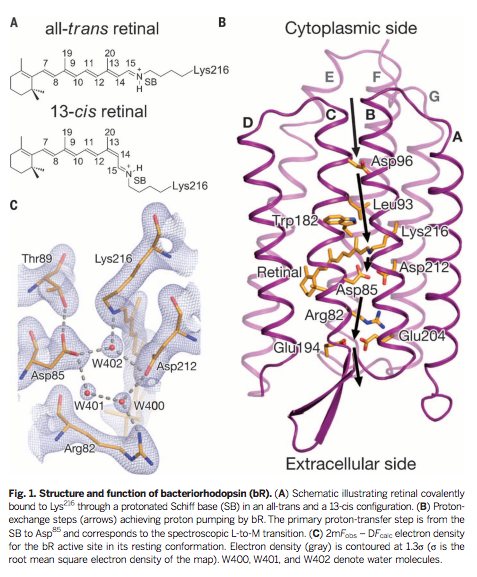
Membrane proteins are popular drug targets, as they are exposed to the environment surrounding the cell. Capturing their movements in video, the authors say, is potentially a revolutionary step forward in drug development.





