Cheetah documentation page 2
Data Analysis
This resource belongs to the Data Analysis group.
Category
Published on
Abstract
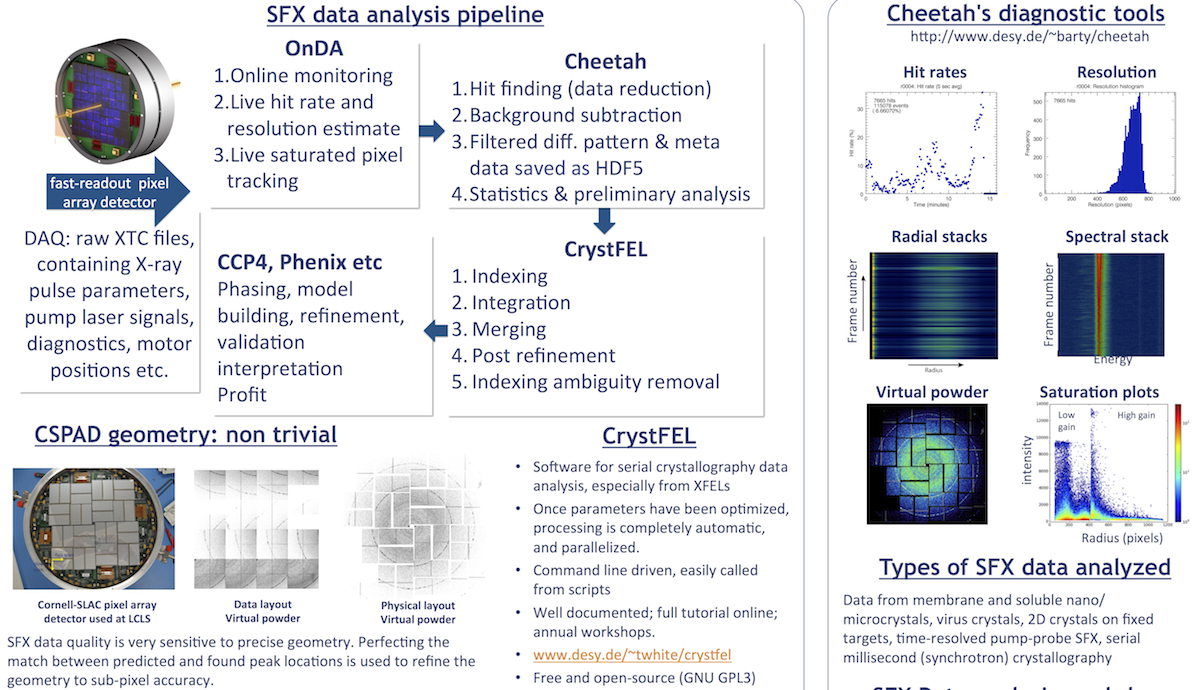
Cheetah documentation Page 2.
Click here for Page 1.
Click here for a list of all keywords.
The official Cheetah website is http://www.desy.de/~barty/cheetah/
These pages will not reproduce all the content from the Cheetah site, but are meant as an addendum.
Running Cheetah without a GUI or the process script
Cheetah can be run on its own, but is most easily used in conjunction with a script such as crystfinder (or process) – which does a lot of useful housekeeping. Here's a quick example of a workflow without using a script:
0) Check that the cheetah program is in your path:
> cheetah -h
If all goes well, you'll see a brief list of Cheetah options. Currently, this is not very helpful, hence the need for this section…
1) Create a new directory, which is where you would like the output of Cheetah will be written.
> mkdir r0090
> cd r0090
2) Make filelist of raw files
Let's say you would like to analyze run 90, in which case there are a few XTC data files in the directory /reg/d/psdm/cxi/cxiXXXX/xtc with names like "e158-r0090-s01-c00.xtc". Firstly, you should write the paths to those files into a text file, which we will then provide to Cheetah as an input:
> find /reg/xtcdir -name '*r0090*.xtc' > xtcfiles.txt
3) Edit your configuration file
In order to run Cheetah, you'll need a configuration file, which contains the instructions and tunable parameters needed to carry out this processing job (more on that later…). Cheetah automatically searches for a configuration file called "cheetah.ini" in the current directory. You may already have a bunch of ".ini" files in your /cheetah/process directory, so you should copy the appropriate .ini file for this job into the current directory
> cp /reg/myinis/test.ini cheetah.ini
4) Now you are ready to run cheetah:
> cheetah -l xtcfiles.txt
Once Cheetah has completed the job, you will find several log files, along with hdf5-formatted data files containing individual "hits", summed "powder" patterns, SAXS profiles, etc. (more on Cheetah output later).
More details coming soon
How to use Cheetah for single particle hit finding, and SAXS / WAXS experiments.
- Psana.cfg
- Psana-spi.cfg: do_gain (yes)
- Psana-spi.cfg: do_peds (yes)
- Psana-spi.cfg: do_cmod (yes)
How to implement Cheetah on non CXI detectors, e.g. Pilatus.
- From http://www.desy.de/~barty/cheetah/Cheetah/Cheetah_at_home.html
- If your data comes from somewhere other than LCLS, Cheetah can be called from code able to read any other file format: it is simply a matter of passing the frame data to Cheetah for processing. Once again, see the developerpages for more details.
- Basic hit finding from Pilatus detectors (cbf output) can be performed with cbf2hdf5, a cbf to HDF5 converter that creates HDF5’s ready for analyzing with CrystFEL.
- Download cbf2hdf5 from http://www.desy.de/~twhite/crystfel/programs.html
Frequently asked questions can be found on Cheetah's official page.
References
PREVIOUS: Cheetah documentation (page 1)
APPENDIX: Cheetah documentation - all keywords
Back to front page: LCLS serial femtosecond crystallography data analysis instructions